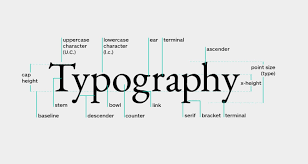
What is Typography:
Typography is a crucial element of graphic design, focusing on the style, arrangement, and appearance of text. It involves choosing the right font, arranging words and sentences, and ensuring readability, impact, and visual appeal. Typography is not just about aesthetics; it influences how a person perceives and interacts with the content. Whether in print, digital media, or advertisements, typography grabs attention and enhances communication. Effective typography helps convey the intended message and creates meaning. It also impacts emotions, evoking different responses depending on font choice, size, spacing, and alignment. Understanding typography’s fundamentals is essential for designers, as it can elevate the overall impact of any design project. Mastering typography enables designers to create more compelling, functional, and visually successful designs. By carefully considering typography, designers can enhance both the aesthetic and functional aspects of their work, ensuring better communication with their audience.
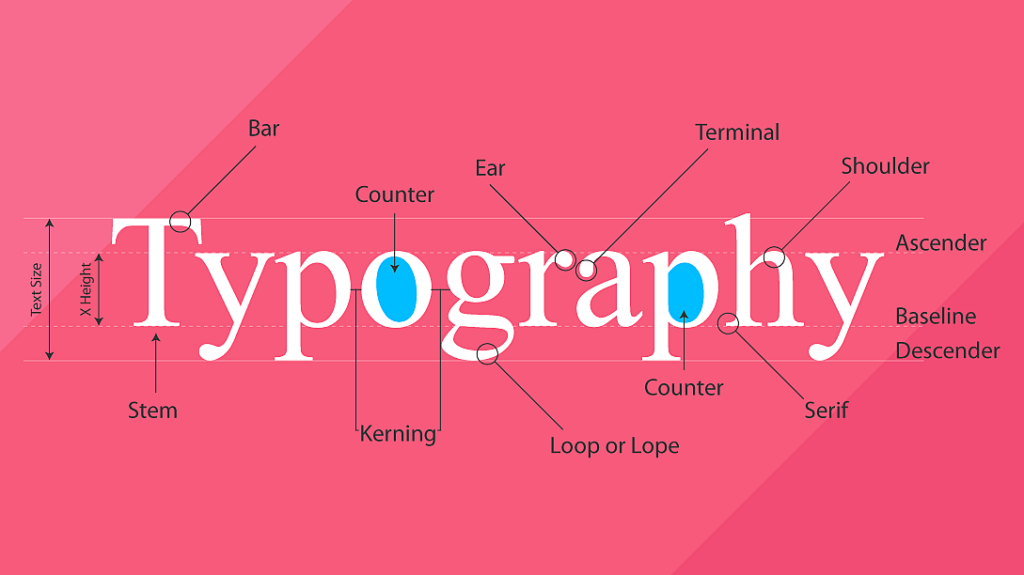
How to use Typography in Graphic Design:
Typography is used in graphic design to communicate messages in a visual and effective way. Designers carefully choose fonts and adjust the layout of text to match the tone, style, and purpose of the design. For example, a professional business logo might use a clean, serif font to communicate trust and authority. On the other hand, a children’s toy store might choose a playful, rounded font to make the design feel fun and friendly. Proper use of typography ensures that the text not only looks good but also supports the overall message of the design.
What Are the Benefits of Typography:
- Improved Readability: The most important benefit of good typography is improved readability. If the text is easy to read, users are more likely to engage with it. Clear, legible fonts make the information accessible and prevent readers from skipping or ignoring content due to difficulty in reading.
- Attracts Attention: Typography can help draw attention to key messages. For example, bold and larger fonts are often used for headings and important information, guiding the viewer’s eye to what matters most.
- Creates a Visual Hierarchy: Typography helps establish a visual hierarchy, organizing information in a way that makes sense. By using different font sizes, weights, and styles, designers can guide the reader’s eye from the most important pieces of information to the least important.
- Supports Brand Identity: Typography can play a big role in building a brand’s identity. Each font has its own personality. When a company uses a specific typography style consistently, it helps reinforce its brand identity and creates a lasting impression on customers.
- Enhances Emotional Connection: Typography can influence the emotional response of the viewer. For instance, an elegant, serif font might make the viewer feel that the brand is classy and sophisticated, while a playful, rounded font might make the brand feel more fun and approachable. Typography helps set the mood for a design and helps strengthen the connection between the brand and the audience.

The right typography is Important:
Purpose: The font you choose should match the purpose of the design. For instance, a corporate document will likely need a formal, clear font, while a creative project like a poster might benefit from a more decorative font.
- Audience: Think about who will be viewing the design. For example, fonts used in children’s books or educational materials should be easy to read and friendly. Meanwhile, fonts used for luxury brands should reflect elegance and sophistication.
- Readability: No matter the style of the design, the text must always be legible. Avoid overly complicated fonts that are difficult to read, especially for body text. Ensure there is enough contrast between the text and the background.
- Consistency: It is important to use typography consistently across a design. Using too many different fonts can make a design feel chaotic and disorganized. Stick to a few complementary fonts that work well together.
- Spacing and Alignment: The way text is arranged is just as important as the font itself. Proper line spacing, letter spacing, and alignment make the text easier to read and visually balanced.
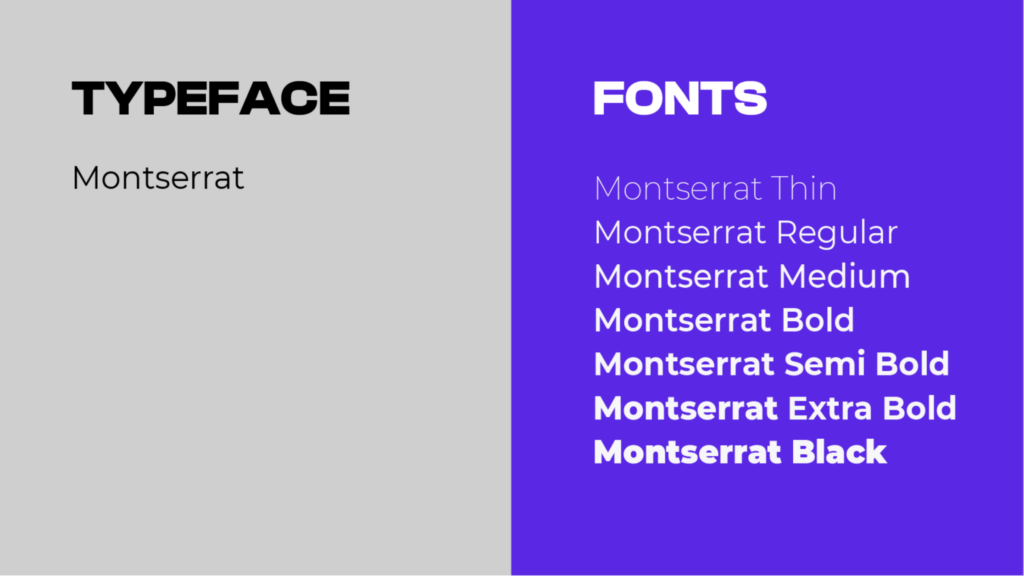
The Different Types of Fonts Used in Graphic Design:
- Serif Fonts: Serif fonts have small lines or “feet” at the end of each letter stroke. These fonts are often used in printed materials, such as books and newspapers, because they are easy to read in long passages of text. Examples include Times New Roman and Georgia.
- Sans-Serif Fonts: Sans-serif fonts do not have the small lines at the end of the strokes. They are often used in digital content because they are easy to read on screens.
- Script Fonts: Script fonts are designed to look like handwritten text. They are often used for invitations, greeting cards, or creative designs that need an elegant or personal touch. Examples include Brush Script and Pacifica.
- Decorative Fonts: Decorative fonts are used for special, creative purposes. They can be playful, unique, or artistic, and are often used for headlines or logos. Examples include Comic Sans and Lobster.

How Typography Affects the User Experience:
Typography plays a significant role in the user experience of a design. It helps users navigate content easily and ensures that information is communicated effectively. Good typography can make the difference between a user enjoying their experience or abandoning the content because it is difficult to read or unattractive.On the other hand, a site with clear, easy-to-read fonts makes it more likely that users will engage with the content and stay longer.

Conclusion:
Typography is much more than just picking a pretty font—it is a powerful tool in graphic design that influences readability, emotional response, and brand identity. By understanding how to use typography effectively, designers can create engaging, clear, and visually appealing designs that communicate messages successfully. The right typography helps improve the user experience, guide the reader’s eye, and strengthen a brand’s presence.